As mentioned in Chapter 1, Section 2, the relationship between human beings and nature is inseparable. Everything on earth is like a tight array of dominoes. The safe balance must rely on the stability of each domino. If one of the dominoes collapses, the entire ecosystem will collapse. Hence, we cannot make climate warming disappear by simply dealing with methane emission of livestock. What dominoes are toppled as a result of people farming hundreds of billions of animals, and huge amounts of greenhouse gases are produced to increase the temperature? This chapter will introduce the impacts of climate warming.
First of all, rising temperatures will cause ice on Earth to melt. Ice sheets is an important part of maintaining ecology of nature environment. Only 2.5% of water on Earth is fresh water. And 70% of that is stored in the ice and atmosphere. These ice sheets will melt and overflow some in warm summer months to provide fresh water for people. In cold winter, they extract the moisture and water of Earth and store it as fresh water ice. Such a cycle is the mechanism by which nature works in balance.
The chain effects of ice melting everywhere are: Melting glaciers in high mountains will cause water shortages in downstream rivers. Melting ice sheets in Arctic and Antarctica will damage local ecology, rise sea levels, reduce land area, and increase the rate of rising temperature. Melting permafrost will release methane from the frozen ground. The conditions of melting ice around the planet are elaborated as follows:
Arctic
Rising air and sea temperature have caused continuous melting of ice sheets in Arctic and Antarctica. The poles are very sensitive to changes in temperature. When the global mean temperature drops, the poles will experience the greatest cooling. Alternatively, the poles will experience the greatest warming when the global mean temperature is higher. This is the phenomenon called, “Polar Amplification”. The reason is that polar regions are mostly covered by ice, which reflects sunlight. When ice sheet shrinks and ocean expands, the dark seawater will absorb more solar radiation and intensify global warming. Ice that has been frozen for tens of millions of years at the poles of Earth is now all in jeopardy.
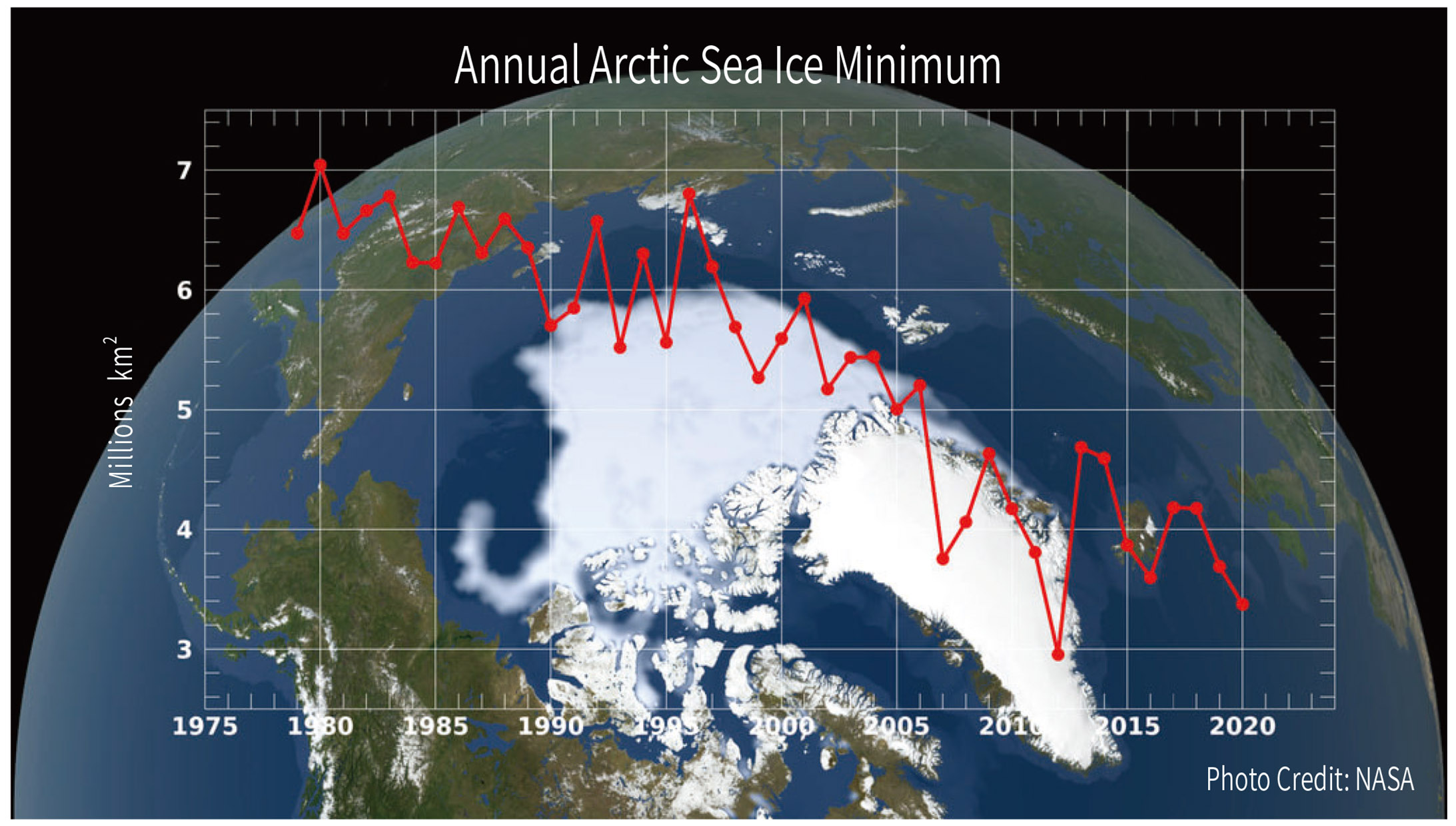
In Arctic, sea ice increases in winter and melts in summer. Over the 40 years since record began, there has been a clear downward trend in annual Arctic sea ice minimum. The lowest record appeared in 2012, and the second record appeared in 2020. In the past 20 years, the Arctic Circle temperature has risen by more than twice the global average (IPCC AR4 WG2). The melting of sea ice directly impacts the Arctic ecosystem and affects all local living beings.
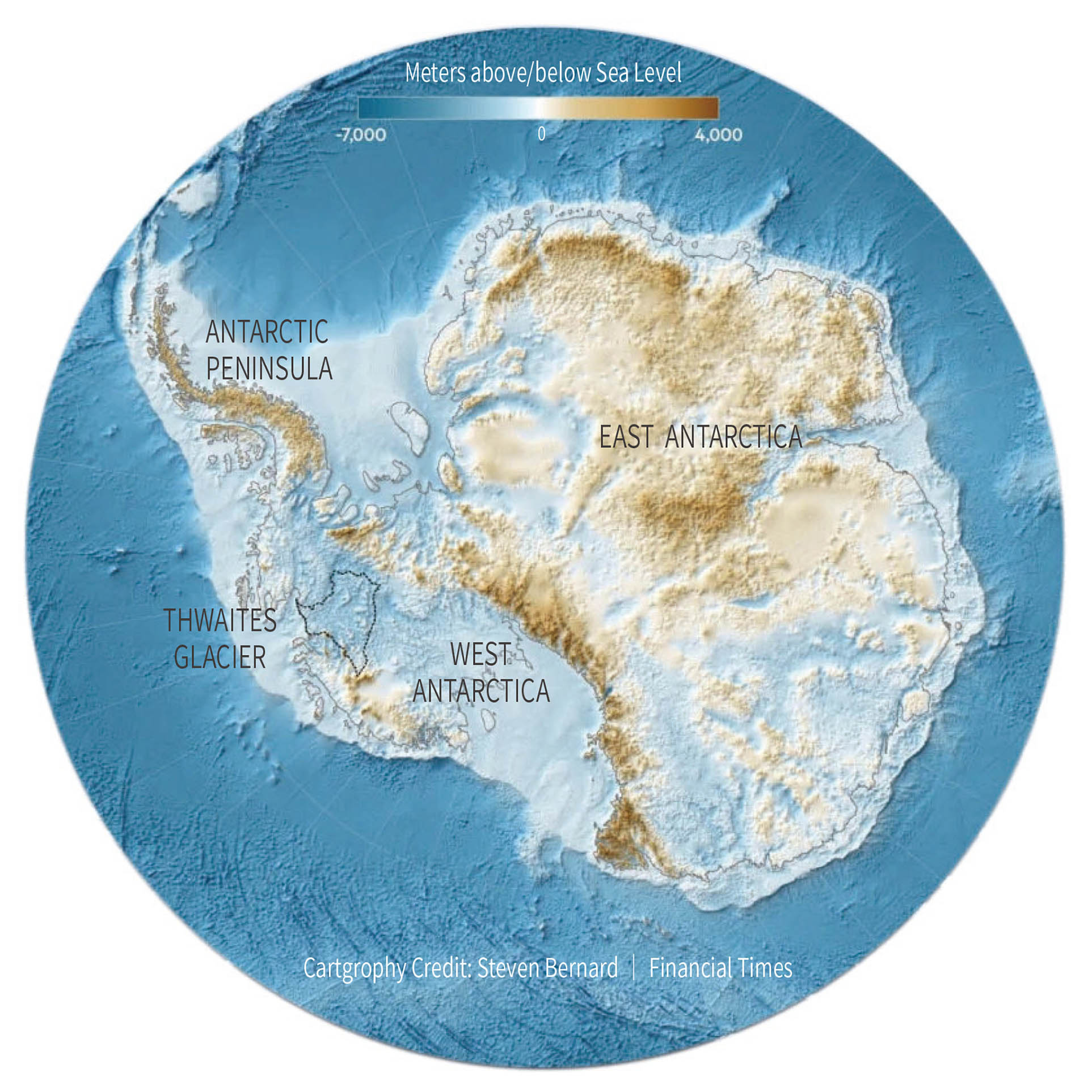
Antarctica
In 2020, a study in the British magazine, Nature Climate Change, pointed out: Over the past 30 years, the heating rate of Antarctica’s interior has been three times the global average. As the tropical ocean temperature rises, it affects Antarctic ocean temperature as well. Air currents over the ocean get warmer. Warm air coupled with more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere caused a rapid temperature rise in the remote Antarctica interior.
If Antarctic ice sheets completely melt, sea level will rise 57-72 meters (Antarctic Thickness Data Report). Here is an Antarctic glacier now on the verge of crumbling: Thwaites. Thwaites Glacier in Antarctica is also known as the “Doomsday Glacier”. It is like a plug, blocking the rest of West Antarctic Ice Sheet from flowing into the ocean. But Thwaites Glacier is getting thinner and thinner. The complete melting of Thwaites Glacier will raise sea level by about 65 cm. If the West Antarctica Ice Sheet melts entirety, global sea levels will rise by 3.3 meters. This is a height that will inundate most coastal cities. Due to the huge influence of Thwaites Glacier, there is currently an International Thwaites Glacier Collaboration (ITGC) dedicated to observe it.
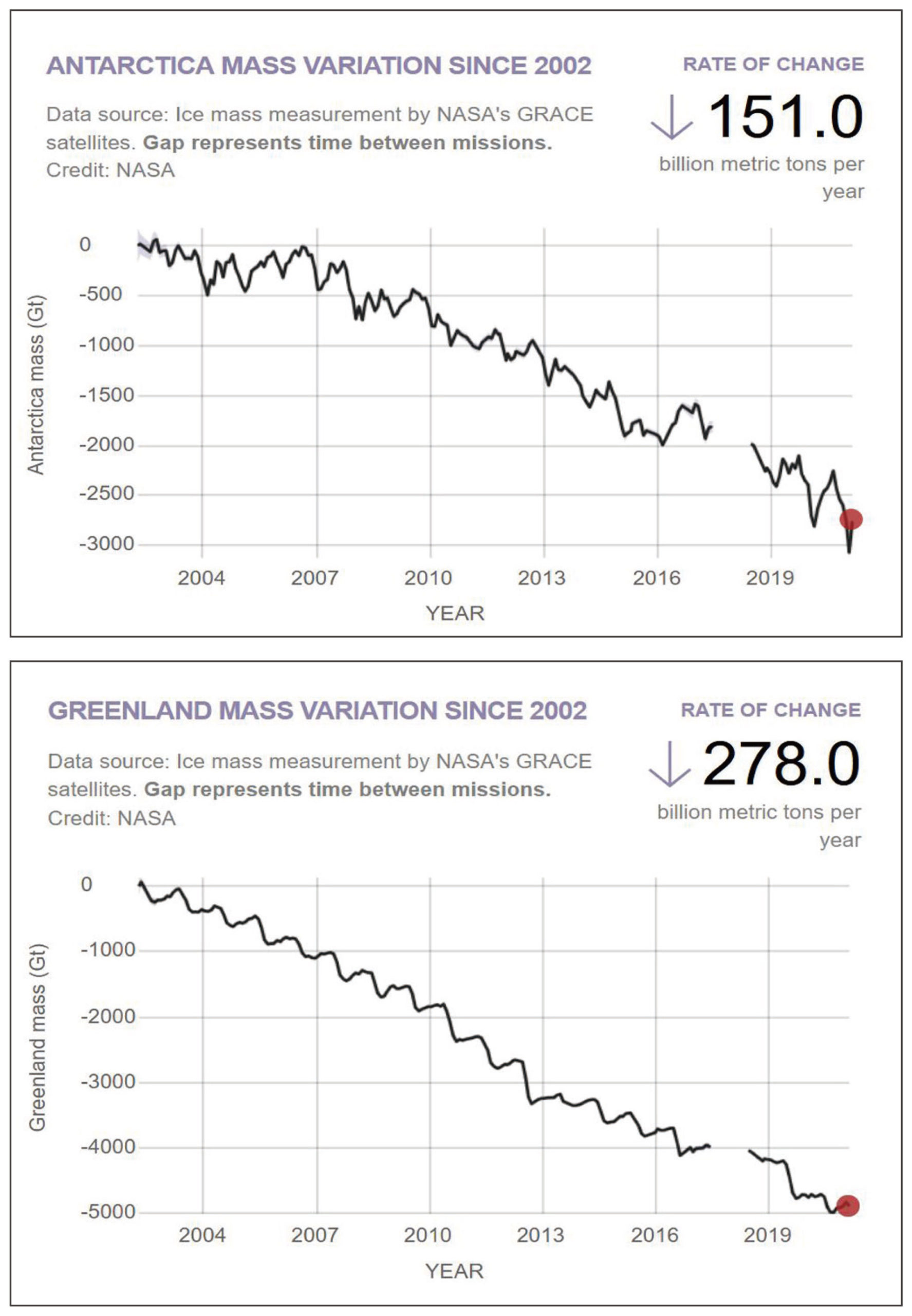
Mass Loss Figures
The figures below are made by NASA using satellite measurements. They clearly show that the mass of Greenland and Antarctica has been decreasing rapidly over the past 18 years. Greenland, in particular, is decreasing at a rate of 278 billion metric tons per year. Antarctica loses less mass because of its lower temperature, but the average mass loss is also as high as 151 billion metric tons per year.
Ice sheets in various places are melting rapidly. Rising sea levels will inundate coastal cities. And more serious is that the expansion in ocean volume will accelerate absorption of heat. Once the ocean warms, it takes tens of thousands of years to cool down. If the internal temperature of Earth Crust increases, it will take hundreds of thousands of years to cool down.
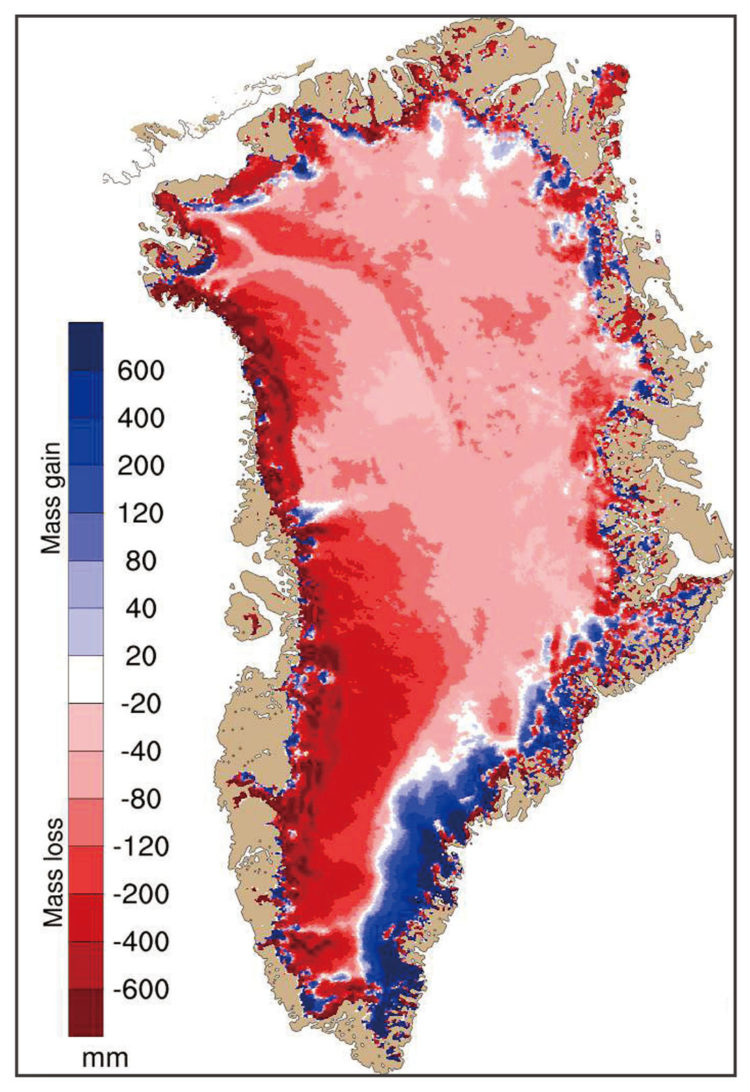
Greenland
Greenland is the largest island on Earth, with eighty percent covered by ice and snow. If the ice sheet entirely melts, sea level will rise 7 meters (Impact of Warming Arctic, Cambridge University).
More than 280 billion tons of melted ice flows from Greenland into the ocean every year. It is the main cause of global sea level rise. According to a 2020 report by researchers from Ohio University of US, Greenland’s ice sheet melting has reached the “point of no return”. It would continue to melt even if the climate crisis were halted. This is the first of a series critical points. As warming continues, the situation will get worse.
The figure on the right is the observation from Climate State Report in 2019 of United Nations World Meteorological Organization (WMO). The statistic period is from September 2018 to September 2019. This figure shows that almost all ice is lower than normal level except in the southeast.
Glaciers in Various Regions
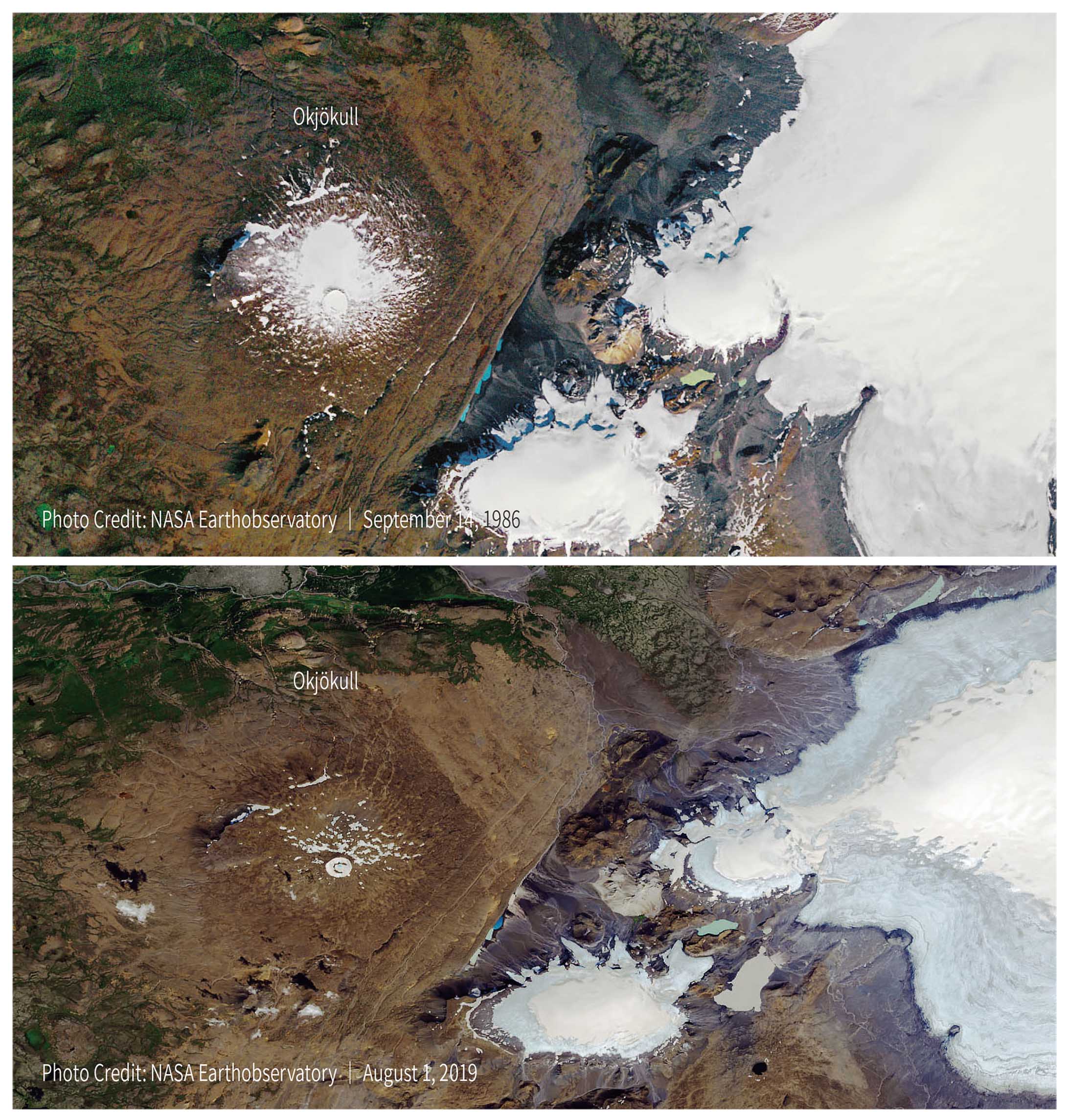
Glaciology has been studied by a lot of people. And numerous before and after pictures of melting glaciers are also taken by many photographers. These information can be easily searched on the Internet. Too many glaciers have disappeared in various regions to be listed out. The following is just an example, the Okjökull Glacier in Iceland.
Ice covers about 10% of Iceland, making it an integral part of the landscape. Loss of glacial ice impacts water resources, infrastructure, and even raises the land altitude. Earth Crust will rebound because of ice mass loss. In severe cases, it will cause frequent earthquakes and volcanic activity. The latter is exactly the current situation in Iceland. According to the news in March 2021, 40,000 earthquakes hit Iceland in a month. And the Fagradals mountain volcano that had been dormant for more 6,000 years erupted again. The Antarctica also experiences frequent earthquakes.

Further Reading: 1-3 Greenhouse Effect and Greenhouse Gases | 1-5 The Real Percentage of Emission | 1-2 The Cost of Meat Eating Habit and Livestock
Cited Reports: The State of Global Climate in 2019 | Annual Arctic Sea Ice Minimum |IPCC AR4 WG2 | Nature-Climate Change Article | Antarctica Thickness Datasets | ITGC | Imapct of Warming Arctic | Greenland-Point of No Return
Relative Download: Diet and Environment Relative Download